Cognitive representations of social networks in isolated villages
Abstract
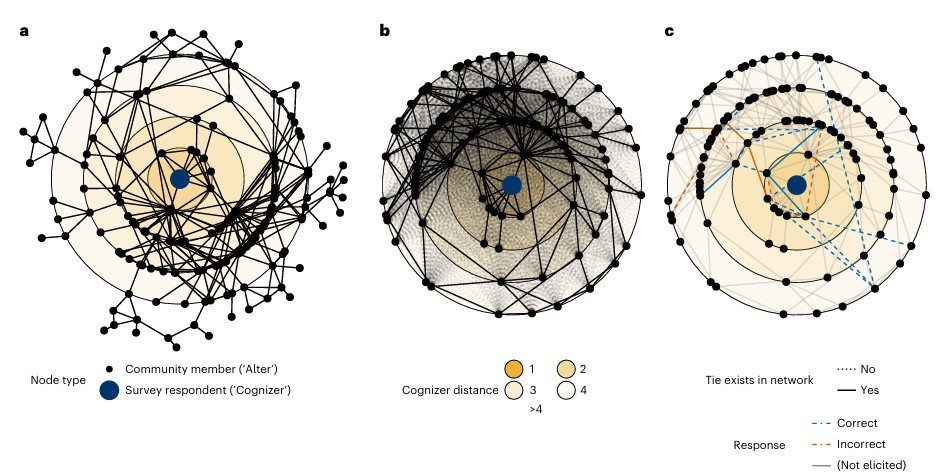
People not only form social networks, they construct mental maps of them. We develop a sampling strategy to evaluate network cognition in 10,072 adults across 82 Honduras villages and systematically map the underlying village networks. In 17 villages, we also discern the genetic relatedness of all 1,333 residents. Observers overestimate the social interactions among kin and are 33.38 percentage points (J) more accurate in judgements of ties between non-kin (95% confidence interval: 31.27–35.49). Counterintuitively, observers had more accurate beliefs about non-kin pairs, especially when the observers were popular, middle-aged, or educated. Observers were less able to accurately judge ties across different religions or wealth. Individuals in villages that cultivate coffee, requiring coordinated effort, demonstrated greater bias to view networks as connected. Finally, more accurate respondents had better access to information that we experimentally introduced to their peers. Overall, people inflate the number of connections in their networks and exhibit varying accuracy and bias, with implications for how people affect and are affected by the social world.
Citation:
Feltham, E., Forastiere, L. & Christakis, N.A. Cognitive representations of social networks in isolated villages. Nat Hum Behav (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-025-02221-6