
Citation:
S.V. Subramaniana, Rockli Kima, Nicholas A. Christakis, "The “average” treatment effect: A construct ripe for retirement. A commentary on Deaton and Cartwright" Social Science & Medicine,

Citation:
S.V. Subramaniana, Rockli Kima, Nicholas A. Christakis, "The “average” treatment effect: A construct ripe for retirement. A commentary on Deaton and Cartwright" Social Science & Medicine,

Citation:
Wu J, Crawford FW, Kim DA, Stafford D, Christakis NA. Exposure, hazard, and survival analysis of diffusion on social networks. Stat Med. 2018 Jul 30;37(17):2561-2585. doi: 10.1002/sim.7658. Epub 2018 Apr 29. PMID: 29707798; PMCID: PMC6933552.

Citation:
H. Shirado and N.A. Christakis, "Locally Noisy Autonomous Agents Improve Global Human Coordination in Network Experiments" Nature, 545, 370–374 (18 May 2017) doi:10.1038/nature22332
Citation:
H.B. Shakya, D. Stafford, D.A. Hughes, T. Keegan, R. Negron, J. Broome, M. McKnight, E. Nicoll, J.A. Nelson, E. Iriarte, J.H. Fowler, and N.A. Christakis, "Exploiting Social Influence to Magnify Population-Level Behavior Change in Maternal and Child Health: A Randomized Controlled Trial of Network Targeting Algorithms in Rural Honduras" BMJ Open, (2017) 7(3), p.e012996.
Citation:
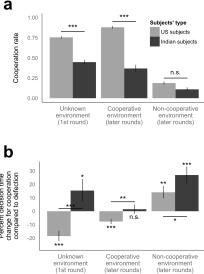
A. Nishi, N.A. Christakis, and D. G. Rand, "Cooperation, Decision Time, and Culture: Online Experiments with American and Indian Participants" PLoS ONE, (February 2017) DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171252

Citation:
H.B. Shakya, N.A. Christakis, and J.H. Fowler, "An Exploratory Comparison of Name Generator Content: Data from Rural India" Social Networks, 48: 157-168 (January 2017)

Citation:
J.N. Rosenquist, S.F. Lehrer, A.J. O’Malley, A.M. Zaslavsky, J.W. Smoller, and N.A. Christakis, "Cohort of birth modifies the association between FTO genotype and BMI" PNAS: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112(2): 354–359 (January 2015) doi: 10.1073/pnas.1411893111
Citation:
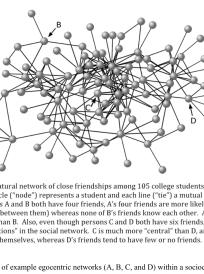
Perkins JM, Subramanian SV, Christakis NA. Social networks and health: a systematic review of sociocentric network studies in low- and middle-income countries. Soc Sci Med. 2015 Jan;125:60-78. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2014.08.019. Epub 2014 Aug 19. PMID: 25442969; PMCID: PMC5690563.

Citation:
A.J. O’Malley, F. Elwert, J.N. Rosenquist, A.M. Zaslavsky, and N.A. Christakis, "Estimating Peer Effects in Longitudinal Dyadic Data Using Instrumental Variables" Biometrics, 70: 506-515 (April, 2014) doi: 10.1111/biom.12172

Citation:
N.A. Christakis and J.H. Fowler, "Social Contagion Theory: Examining Dynamic Social Networks and Human Behavior" Statistics in Medicine, 32(4): 556-577 (February 2013); http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/sim.5408